LESÕES DOS JOELHOS
Painful Knee Prosthesis
Pain that may persist since the surgery or appear later
LESÕES
DO JOELHO
INFEÇÕES OSTEOARTICULARES
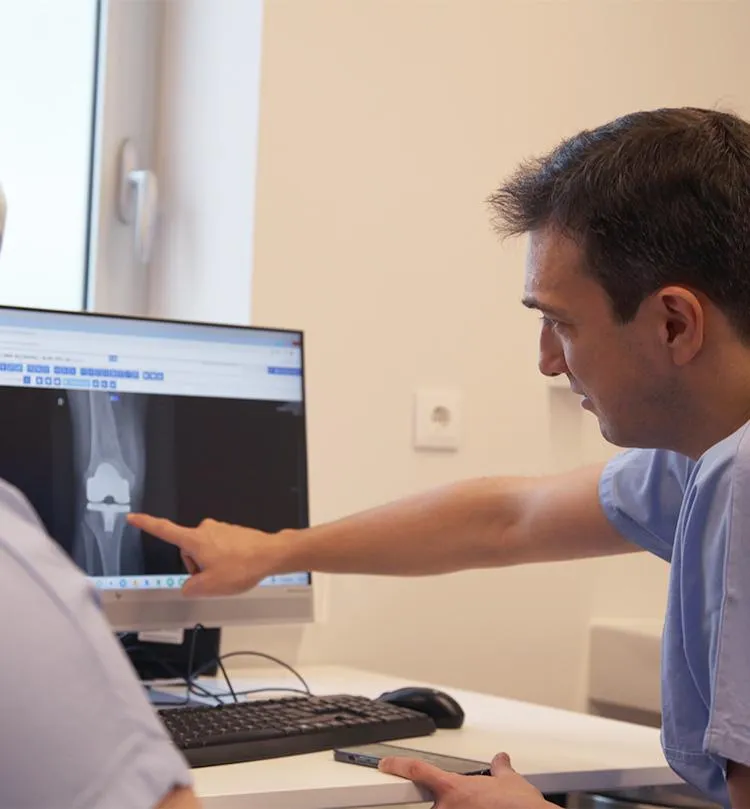

Knee Injuries - Degenerative Pathology
Painful Knee Prosthesis
Painful Knee Prosthesis
Total knee replacement is considered one of the most successful orthopedic surgeries. Pain relief and functional improvement are generally excellent. However, a small proportion of patients report pain that may persist since the surgery or appear later. Due to the positive clinical outcomes, the number of patients with knee prostheses has increased, which naturally means that more people experience pain in the operated knee.

Causes
The cause of the pain is not always the operated knee itself. Other issues such as spinal, hip, or even arterial diseases can justify the pain, especially in cases where the pain remains the same as it was before the placement of the prosthesis.
However, in most cases of painful knee prosthesis, the cause indeed lies in the operated knee. In addition to technical issues related to poor placement of the original prosthesis, the most common causes of pain following total knee replacement include:
The cause of the pain is not always the operated knee itself. Other issues such as spinal, hip, or even arterial diseases can justify the pain, especially in cases where the pain remains the same as it was before the placement of the prosthesis.
1) Loosening: This is a process in which the prosthesis is no longer securely attached to the bone due to mechanical failure or significant trauma.
2) Infection (ften referred to as rejection): This occurs when bacteria lodge in the prosthesis and cause an inflammatory reaction in the body against them.
3) Instability: This is a situation where there is abnormal and excessive movement of the prosthesis due to insufficient support from the knee ligaments.
4) Patella Problems: The patella is part of the extensor apparatus (responsible for straightening the leg) and plays a crucial role in the flexion-extension movement of the knee. If this movement is not harmonious, pain can occur.
5) Stiffness: This is a situation where the knee lacks the necessary mobility to perform activities required in daily life.
Symptoms
In addition to pain, a variety of other symptoms can accompany the failure of a total knee prosthesis. Depending on the cause, the pain may be accompanied by a sensation of instability (i.e., feeling the knee is failing) or excessive stiffness (the knee being unable to fully extend or flex).
It is also common to experience an associated effusion, often referred to as a swollen knee.
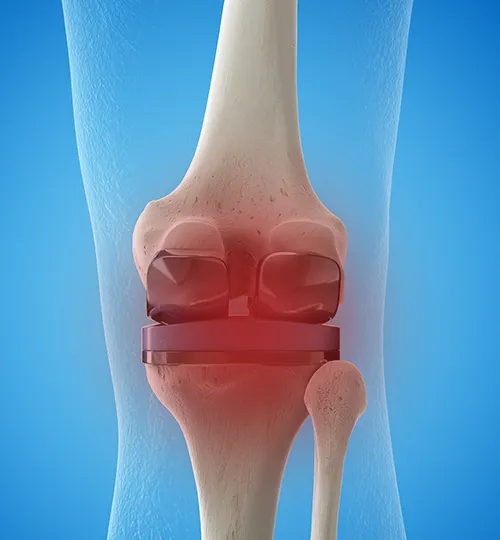
Diagnosis
While the diagnosis may be apparent in cases such as advanced loosening, intense instability, or certain infections, a rigorous and detailed investigation is required in a significant proportion of cases.
The clinical history and physical examination are the initial steps and may indicate one of the various underlying issues. However, in most cases, further investigation with radiographs (important to compare with previous radiographs), blood tests, and analysis of fluid obtained from the knee will be necessary. Depending on the situation, it may also be necessary to perform a CT scan or other tests such as Nuclear Medicine exams.
Treatment Options
The vast majority of causes of painful prosthesis can be treated.
Most commonly, the solution involves revision surgery. However, the success of the procedure largely depends on accurately identifying and correcting the cause that led to the failure of the initial prosthesis. The approach varies depending on the cause of the pain.
In instances where it is not possible to identify or resolve the issue, specialized pain management may be a more effective solution than undertaking repeated revision surgeries without resolving the underlying problem.
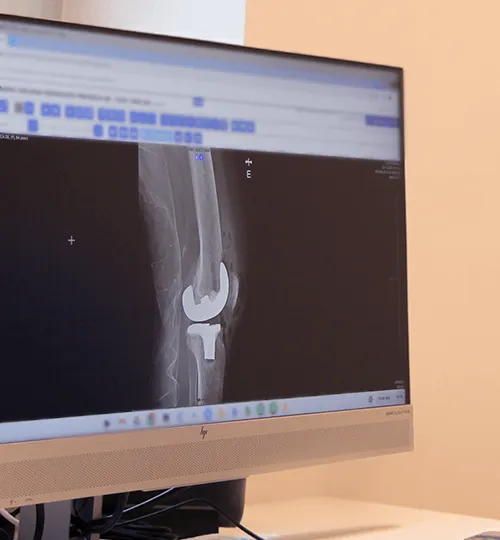
Structured and unique approach in Portugal!
Copyright © 2026 Ricardo Sousa Ortopedia All rights reserved
Copyright © 2026 Ricardo Sousa Ortopedia
All rights reserved
Powered by Pointfull.




